Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
If you’ve explored the world of cryptocurrencies, you’ve likely noticed the term “txns” used everywhere from Etherscan to Coinbase to Binance. “Txns” is shorthand for “transactions,” a core pillar of how digital currencies move and operate on blockchains. This abbreviation pops up throughout crypto exchanges, wallet interfaces, and most major block explorers, helping users quickly assess transaction activity.
Whether you’re a complete beginner monitoring your first wallet or an experienced trader diving into DeFi, understanding the language of crypto is crucial.
In 2025, as crypto adoption rises, knowing key terms like “txns” can offer an edge in security, costs, and basic navigation. This guide is designed to be your all-in-one, up-to-date reference for everything about “txns” from what the term means, to how transactions actually work, and why decoding them matters for every crypto user.
In crypto, “txns” stands for “transactions” the fundamental actions of sending, receiving, or interacting with digital assets on a blockchain. Abbreviations like “txns” (plural) or “txn” (singular) are common due to space constraints on screens and APIs, as well as the fast-paced, digital-focused nature of the industry. You’ll see these terms in wallets, data consoles, and block explorers, e.g., {"txns": 2,145} in an API response.
This basic understanding is the foundation for figuring out how transactions work across different blockchain platforms.
Every crypto transaction is a digital message instructing the blockchain to move value or execute an operation. Here’s how a typical process unfolds:
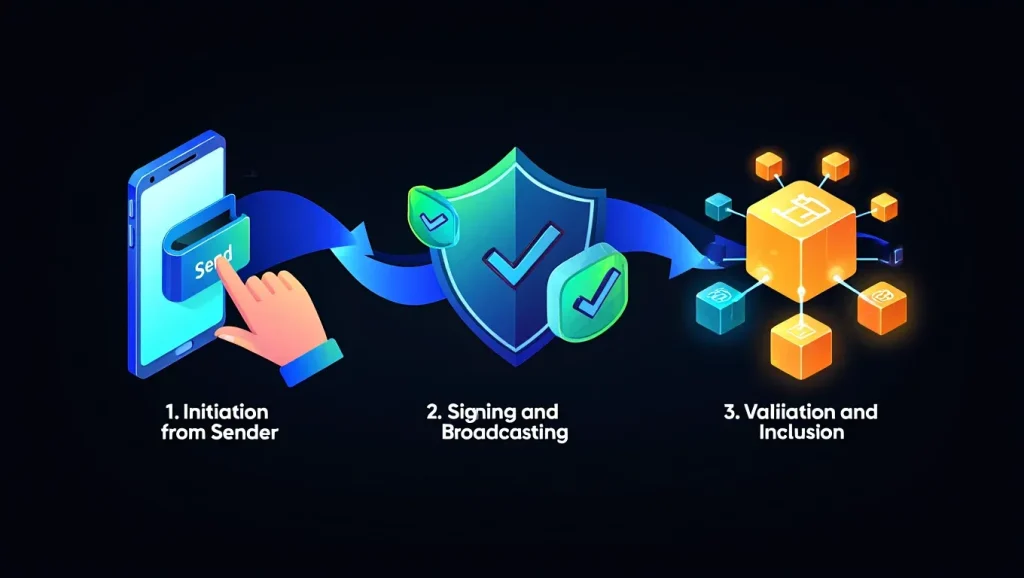
The user, via a wallet or exchange, creates a txn. Essential details include:
The wallet cryptographically signs the transaction and broadcasts it to the blockchain’s peer-to-peer network. Signing proves ownership and protects against unauthorized transactions.
Nodes temporarily store the txn in a “mempool.” Miners (Proof of Work) or validators (Proof of Stake) select txns to include in the next block according to rules and fees offered. Blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum may structure txns differently, but the logic is similar: the network confirms ownership and ledger changes before finality.
Example Flowchart
| Step | BTC Example | ETH Example |
|---|---|---|
| Initiation | User enters receiver address and sends 0.5 BTC | User submits 1 ETH transfer |
| Signing | Wallet signs txn with private key | Wallet signs + optionally adds a note/data |
| Broadcast | Sent to Bitcoin nodes | Sent to Ethereum nodes |
| Included in Block | Miner includes in next block | Validator adds to block |
| Confirmation | After 1+ confirmations | After 12+ confirmations* |
*Confirmation count varies by asset and value. This overview sets up further detail on how txns are permanently logged on blockchains.
Blockchains act as decentralized, immutable ledgers, recording every transaction (“txn”) in a series of connected blocks. Each block, created at regular intervals (e.g., Bitcoin every ~10 minutes, Ethereum every ~12 seconds), collects new transactions and cryptographically links to the previous block, preventing tampering or retroactive changes.
Blockchains are public by default meaning anyone can read transaction records via block explorers like Etherscan or Blockchain.com. While you see sender and receiver addresses, wallets and real names aren’t directly tied, offering pseudonymity but not true anonymity.
On-chain vs. Off-chain Transactions
| Type | Visibility | Example |
|---|---|---|
| On-chain | Permanent, public, auditable | Bitcoin/Ethereum transfer |
| Off-chain | Not instantly on blockchain | Layer 2 swaps, exchange balance updates |
For example, viewing a BTC transaction on Blockchain.com will show details like: amount, sender, recipient, status, and confirmations. Ethereum explorers go further, letting you see gas fees, smart contract calls, and even decoded data fields. This public accounting offers both transparency and a strong defense against fraud, but requires users to be mindful about privacy.
See more related articles:
| Status | Meaning | Example (Explorer View) |
|---|---|---|
| Pending | Not yet included in a block | “Pending” in MetaMask/Etherscan |
| Confirmed | Accepted, part of the blockchain | 3+ confirmations shown |
| Failed | Rejected (e.g., ran out of gas/on-chain logic failed) | “Failed” status; fee may still be deducted |
Recognizing the type and status of a crypto transaction helps you accurately track your assets and troubleshoot issues quickly.
Key actors include miners (Bitcoin, older Ethereum) and validators (Ethereum 2.0, Solana, Polygon). Transaction speed depends on blockchain design, congestion, and supplied fees.
| Blockchain | Block Time | 1st Confirmation |
|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin (BTC) | ~10 min | ~10 min |
| Ethereum (ETH) | ~12 sec | ~12 sec |
| Solana | ~0.4 sec | <1 sec |
Paying higher fees usually speeds up confirmation. However, network congestion like during NFT drops or market spikes can slow things down. Understanding each step demystifies why txns may “get stuck” or require patience.
Related reads to deepen your knowledge: Parabolic meaning in crypto
Transaction fees are what you pay to have your transaction (txn) processed securely on a blockchain. They discourage spam, reward miners/validators for their work, and align network priorities.
How are fees calculated?
| Blockchain | Avg. Fee (2025)* |
|---|---|
| Bitcoin (BTC) | $0.40–$8 |
| Ethereum (ETH) | $0.20–$10 (Layer 1) |
| BSC | <$0.10 |
| Polygon | <$0.05 |
*Actual figures depend heavily on network activity and sent amounts.
Tips: Many wallets allow you to choose between slow (cheaper) and fast (pricier) fee settings. Always check fee previews before confirming a crypto txn, especially when using DeFi or NFTs where costs fluctuate rapidly.
Every crypto transaction is secured by advanced cryptography. Digital signatures validate ownership, and strong hash functions truly lock data in place meaning past can’t be secretly changed or forged.
However, while blockchain promises transparency, it doesn’t guarantee privacy. All on-chain transactions are visible to anyone. They are “pseudo-anonymous”: addresses aren’t tied to names, but advanced analytics can sometimes de-anonymize patterns.

Common privacy misconceptions:
Some users use mixers, privacy layers, or opt for privacy-focused blockchains, but be aware: nothing replaces personal caution and understanding risks before sending crypto.
Many crypto mishaps stem from not understanding transactions: for example, irreversible transfers to a typo address, or falling for phishing txns disguised as legit dApp calls. Mastering gives you tools to verify claims, catch red flags, and invest or trade with confidence in today’s fast-moving crypto trends.
Tracking crypto is straightforward with the right tools. Block explorers are web services that let you search and verify every transaction, block, and contract on a blockchain. Leading examples include Etherscan (Ethereum), Blockchain.com Explorer (Bitcoin), and specialized DeFi explorers for protocols like Uniswap or Solana.
txn hash) in your wallet or exchange app.| Explorer | Finds These Fields |
|---|---|
| Etherscan | Hash, sender, receiver, value, gas, confirmations, contract calls, internal |
| Blockchain.com | Hash, inputs/outputs, amount, status, time, confirmations |
| Solscan | Status, block, fee, instruction breakdown, memos |
Check explorer guides or screenshots for extra context. Each blockchain displays fields a bit differently, but the overall flow search hash, read status, verify details remains consistent. This habit is invaluable for tracking funds and resolving disputes or delays.
It’s waiting to be included in a block. This might be due to network congestion or too low a fee. Try increasing the fee for faster confirmation.
No. Once confirmed, blockchains are immutable. Always double-check recipient addresses and amounts before sending.
Timing varies: Bitcoin averages 10 minutes per block, Ethereum about 12 seconds, Solana under a second. Network conditions like congestion and fees can impact speed.
Not truly. Most are pseudonymous: public but not directly linked to identities. Privacy coins offer more obfuscation, but aren’t the norm.
The assets are lost. There’s no central authority to retrieve crypto sent to a mistyped or wrong address.
Typically, you pay fees whether a txn succeeds or fails (e.g., failed Ethereum txns).
A unique identifier proving your transaction exists. Use it to check status on explorers.
Some wallets let you “replace” or speed up stuck pending by using a feature called Replace-by-Fee or creating a conflicting higher-fee txn. Not always possible after the transaction is confirmed.
| Txn, txns | Abbreviations for “transaction(s)”, meaning activities like sending, receiving, or smart contract calls |
| Blockchain | Decentralized ledger that records all crypto txns |
| Wallet | Software/hardware used to store and manage crypto assets and initiate txns |
| Miner/validator | Network actors who include txns in blocks and secure the chain |
| Gas fee | Fee paid to process and confirm txns (especially in Ethereum and EVM chains) |
| Confirmation | When a txn is included in a block and thus considered valid |
| Explorer | Online tool for searching blockchain data and verifying txns |
| Smart contract | Self-executing code running on the blockchain managing more complex txns |
Understanding “txns” in crypto is no longer optional it’s an essential part of navigating the ever-evolving world of digital assets in 2025 and beyond. From grasping simple payments and tracking fees, to decoding explorer data for safety and troubleshooting, mastering transaction basics empowers you to manage risks, save money, and move forward with confidence. Whether you’re investing for the long term or just getting started, building a strong foundation in transaction know-how sets you up for a safer, smarter crypto journey.
At Webtaichinh, our mission is to provide you with clear, unbiased insights into the world of cryptocurrency through the Cryptocurrency category, helping you navigate complex topics with confidence, without hype or hidden agendas.
Webtaichinh delivers real-time financial updates, ensuring you stay informed about market trends, policies, and global economic developments. As part of our commitment to excellence, we provide accurate information and in-depth analysis, empowering investors to make swift, confident decisions in a dynamic financial world.
For inquiries or personalized assistance, feel free to contact us:
📞 Phone: 055 937 9204
📧 Email: webtaichinh@gmail.com
💻 Website: https://webtaichinh.vn/
📍 Address: 13 Ho Tung Mau, An Binh, Di An, Binh Duong
At webtaichinh, your financial success is our mission.