Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

In forex trading, one of the most common questions new traders ask is what is buy limit in forex and how it can improve their trading performance. A buy limit order allows traders to purchase a currency pair at a predetermined price below the current market level, making it a powerful tool for entering trades at more favorable prices.
Mastering this order type helps traders take advantage of market pullbacks, manage risks more effectively, and build strategies that align with long-term success.
A buy limit order in forex is an instruction to purchase a currency pair only at a price lower than the current market price. This means the order remains pending and will execute only if and when the market price drops to or below the specified limit price.
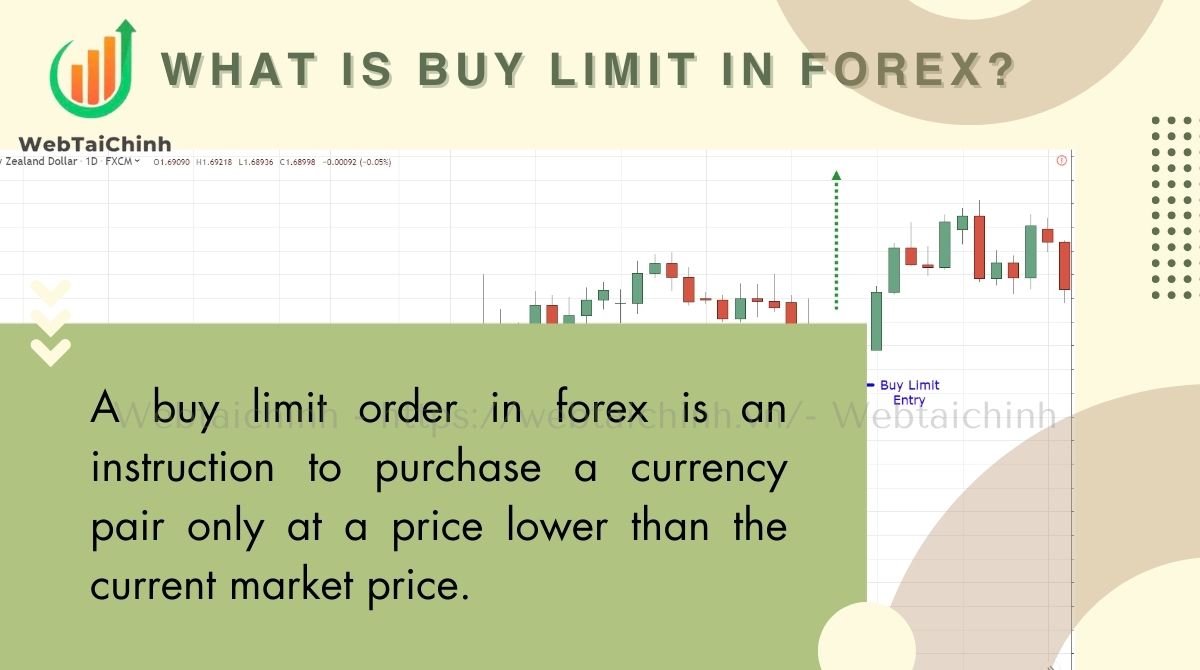
Key attributes of a buy limit order include:
It’s important to distinguish a buy limit order from similar terms: while a limit order can be either buy or sell, a buy limit specifically refers to buying below the market. Additionally, it differs from a pending order, which is a broader term that includes buy limits, sell limits, buy stops, and sell stops.
For example, if EUR/USD is trading at 1.1000, placing a buy limit at 1.0950 means your order will only execute if the price falls to 1.0950 or lower.
Now that we understand what is buy limit in forex, we should also learn how a buy limit order works as it can help you take advantage of falling prices and improve your timing. Here is a step-by-step outline:
Forex brokers may use different order book models. Some display your pending buy limit orders publicly, while many retail brokers keep them hidden, simulating the order book internally. This can affect how orders fill, especially during volatile market conditions.
Most trading platforms allow you to set expiration options such as GTC (Good Till Cancelled), day orders (expire end of trading day), or custom expiration times. Choose according to your trading strategy and timeframe.
Partial fills can occur if the available liquidity at your limit price is insufficient to fill your full order size. This is more common with large trades or during less liquid trading hours.
Knowing when to apply a buy limit order is just as important as understanding how it works. The effectiveness of this order type largely depends on market context, trading strategy, and technical signals.
By identifying the right situations, traders can secure better entry points, improve risk-to-reward ratios, and avoid common pitfalls that lead to missed or poorly executed trades. Below are the key scenarios where buy limit orders prove most useful and when you should avoid them.
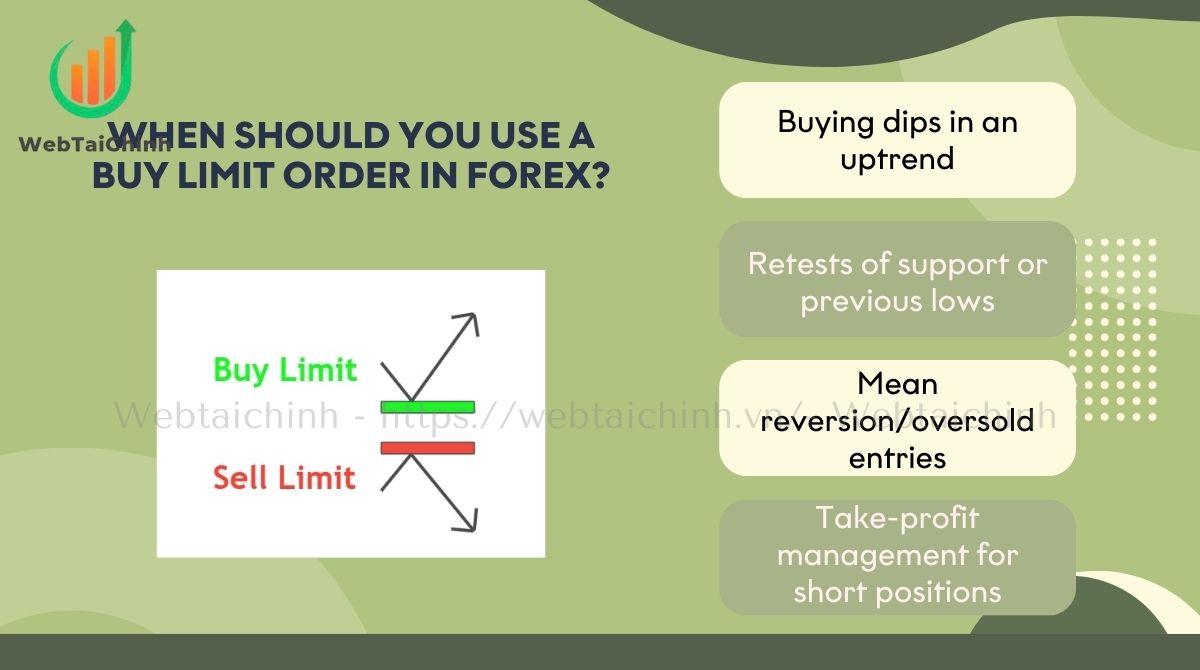
When not to use buy limits: Avoid placing them during breakout attempts, high-impact news spikes, or in markets with thin liquidity, as prices may rapidly bypass your limit or fail to fill.
Understanding buy limit orders becomes much clearer when you see them in action. Real-world examples with specific prices and trade setups demonstrate how traders apply this tool to capture better entries, manage risk, and maximize profit potential.
Below are practical scenarios across popular currency pairs that show how buy limit orders can be used effectively in different market conditions.
Not all order types in forex serve the same purpose, and understanding their distinctions is crucial for building a flexible trading strategy. While a buy limit helps you catch retracements, a buy stop is designed for breakouts, and a market order provides immediate execution.
Comparing these three side by side allows traders to see their unique strengths, limitations, and best-use cases, ensuring the right order is chosen for the right market condition.
| Order type | Placement price | Execution | Use case | Pros | Cons |
| Buy limit | Below current price | Executes at limit price or better when price falls to limit | Buying dips, pullbacks | Price control, entry at better price | May not fill if price doesn’t reach |
| Buy stop | Above current price | Executes at stop price or worse when price rises to stop | Breakouts, momentum entries | Capture momentum | Potential slippage, less price control |
| Market order | Current market price | Executes immediately at market | Immediate entry/exit | Fast execution | Slippage risk, no price control |
In practice, use buy limits to enter on retracements, buy stops for breakouts, and market orders if you want instant execution regardless of price. Each serves a distinct tactical purpose.
Placing a buy limit order may sound complex at first, but most trading platforms make the process straightforward. By following a clear set of steps, traders can ensure their orders are entered correctly and aligned with their strategy. The process is largely the same across popular platforms like MetaTrader, cTrader, or TradingView, making it easy to apply regardless of where you trade.
These steps apply broadly across platforms like MetaTrader 4/5, cTrader, and TradingView. Utilizing alerts and confirmations can help avoid missed trades and clarify order execution status.
While buy limit orders offer strong price control and strategic entries, they are not without risks. Market volatility, liquidity gaps, and broker policies can all affect whether your order gets filled as intended. Understanding these limitations is critical so you can anticipate potential issues and adapt your risk management accordingly.
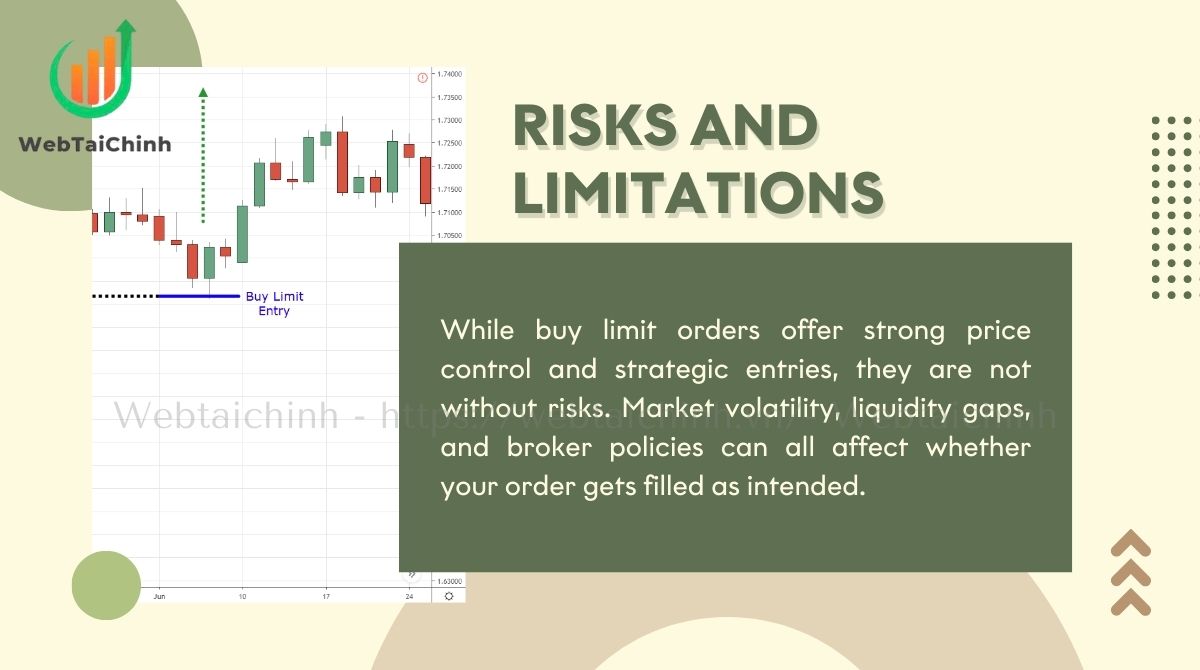
These realities mean buy limit orders are not foolproof and require careful monitoring alongside sound risk management.
Beyond the basics, using buy limit orders successfully requires precision and discipline. Experienced traders often combine technical analysis with smart order placement techniques to maximize effectiveness. By applying proven tips and avoiding common mistakes, you can turn buy limit orders into a reliable tool for consistent trade execution.
A buy limit in forex is an order to buy below the current market price. For example, if EUR/USD is at 1.1000, you can place a buy limit at 1.0950 to enter only if price drops.
A buy limit works by staying pending until the market price falls to or below your set level. Once triggered, it executes at your limit price or better.
Neither is universally better; it depends on strategy. Buy stops suit breakout trading above market price, while buy limits are best for buying pullbacks below market price.
If GBP/USD trades at 1.3000 and you expect a dip to 1.2950 before rising, you place a buy limit at 1.2950. The order fills only if price drops to that level.
Read more:
To sum up, understanding what is buy limit in forex is essential for traders who want greater control over their entries and improved risk management. By learning when to apply buy limit orders, recognizing their limitations, and following best practices, you can enhance your trading strategy and avoid costly mistakes.
For more in-depth guides and expert insights into forex and broader financial topics, visit webtaichinh — your trusted destination for Forex Education and financial knowledge.
Web Tai Chinh is a portal that updates news and information related to finance quickly and accurately, helping users have an overview before investing, clearly understanding concepts and terms related to Finance. Explore more insights in our Forex category, start your FX trading journey today with the right partner for long-term success.
📞 Contact: 055 937 9204
✉️ Email: webtaichinhvnvn@gmail.com
📍 Address: 13 Ho Tung Mau, An Binh, Di An, Binh Duong