Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

What is free margin forex and why does it matter for your trading success? Free margin in forex is the portion of your account equity that’s not tied up in open positions your ava ilable “buying power” to open new trades or cushion against market swings. Without enough free margin, you risk hitting a margin call, forcing your broker to close trades at a loss.
This guide from Webtaichinh will show you exactly what free margin is, how it works, and how to manage it effectively so you can trade with confidence and avoid costly forced liquidations.
What Is Free Margin Forex? Free margin in forex represents the portion of your account equity that’s not locked in open positions. It’s the capital you can still use to open new trades or to absorb losses without triggering a margin call. In other words, it’s your available “trading power” after deducting the margin already committed to active positions.
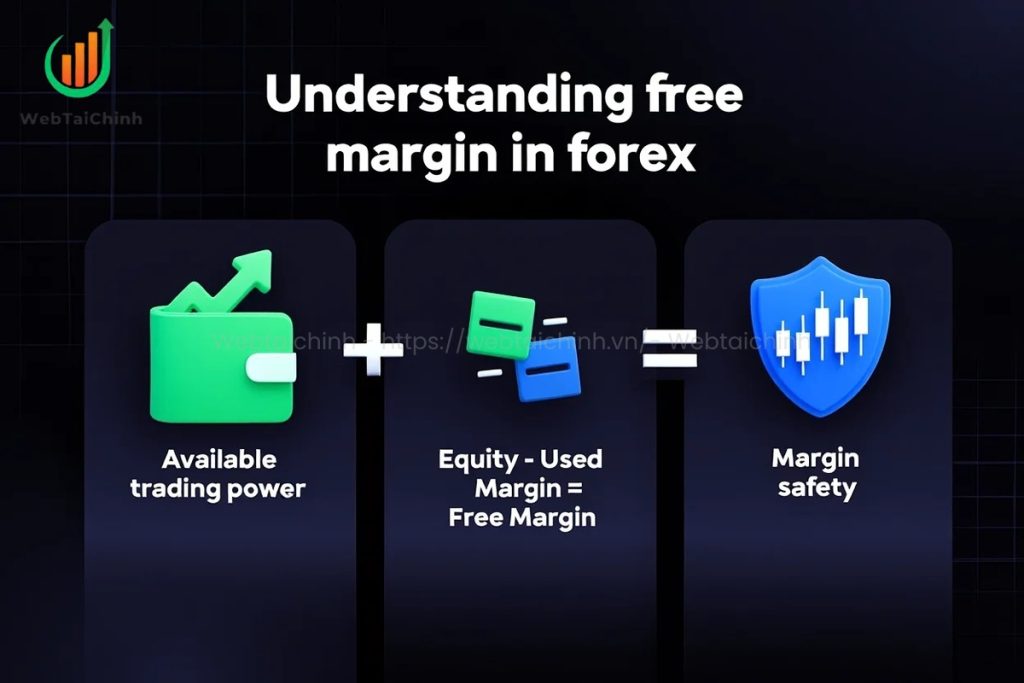
Free margin is calculated as the difference between your account equity and the used margin. If you have no open trades, your free margin equals your entire account balance. If you have active trades, the free margin will change in real time based on floating profits and losses.
Maintaining adequate free margin ensures you can keep positions open during market fluctuations and seize new opportunities when they arise.
The standard formula to calculate free margin in forex is:
Free Margin = Equity – Used Margin
Where:
Equity = Account Balance ± Floating Profit/Loss
Used Margin = Margin locked as collateral for all open positions
Before mastering free margin, it’s important to understand these related concepts:
Balance: Your account value excluding floating P/L.
Equity: Balance plus or minus the value of open positions.
Used margin: The portion of equity set aside as collateral for current trades.
Margin level: The ratio of equity to used margin, usually expressed as a percentage.
Margin call: A broker warning when your margin level falls below a preset threshold.
In forex trading, free margin is more than just a number on your screen it’s the safeguard that keeps your account alive. Understanding what is free margin forex helps you trade confidently, avoid forced liquidations, and maintain flexibility.

Here’s why it matters:
Opens trading opportunities – High free margin means you can place new trades or scale into winning positions without restrictions.
Prevents margin calls and stop-outs – A healthy buffer allows you to survive drawdowns without triggering broker intervention. A forced stop-out in forex is similar to what does liquidation mean in crypto both protect the platform from excessive losses.
Supports smart risk management – Tracking free margin helps you control leverage, size positions correctly, and avoid overexposure.
Withstands market volatility – Extra capacity gives you room to hold trades through sudden price swings instead of closing at a loss.
Keeping your free margin strong is one of the simplest yet most powerful habits to protect both your capital and your trading mindset.
Knowing what is free margin forex is only the first step you also need to calculate it accurately and track it in real time. This ensures you can manage positions, avoid margin calls, and adjust your strategy before account health becomes critical.
Step 1: Determine account equity
Equity=Account Balance±Floating Profit/Loss\text{Equity} = \text{Account Balance} \pm \text{Floating Profit/Loss}
This reflects the real-time value of your account, including open trades.
Step 2: Identify used margin
Used margin is the collateral your broker holds for all active trades, calculated based on trade size and leverage.
Step 3: Apply the free margin formula
Free Margin=Equity−Used Margin\text{Free Margin} = \text{Equity} – \text{Used Margin}
This gives you the amount of funds available for new trades or to absorb losses.
Example 1: No open trades
Balance: $5,000
Floating P/L: $0
Used Margin: $0
Equity = $5,000 + $0 = $5,000
Free Margin = $5,000 – $0 = $5,000
Here, your entire balance is free margin.
Example 2: Open trades with floating profit
Balance: $5,000
Floating Profit: +$300
Used Margin: $1,000
Equity = $5,000 + $300 = $5,300
Free Margin = $5,300 – $1,000 = $4,300
Profits increase equity, boosting free margin.
Example 3: Open trades with floating loss
Balance: $5,000
Floating Loss: -$600
Used Margin: $1,000
Equity = $5,000 – $600 = $4,400
Free Margin = $4,400 – $1,000 = $3,400
Losses shrink equity, reducing free margin and increasing margin call risk.
MetaTrader 4/5:
Go to the “Trade” tab at the bottom terminal. Free margin is displayed alongside Equity and Margin.
cTrader:
Found in the account summary section on the left sidebar.
Custom broker platforms:
Location varies check “Account Summary” or “Margin Overview.”
Set platform alerts to notify you when free margin falls below a set threshold (e.g., 50% of equity) to take corrective action in time.
When learning what is free margin forex, it’s important to understand how it differs from used margin and margin level. These three metrics work together to determine your account’s trading capacity and risk status.
| Term | Definition | Formula / Display | Impact on Trading |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free margin | Equity not tied up in open positions available for new trades or absorbing losses | Equity – Used Margin | High free margin = more trading capacity; low free margin = risk of margin call |
| Used margin | The portion of equity locked as collateral for current trades | Sum of required margin for all positions | Higher used margin reduces free margin |
| Margin level | The ratio of equity to used margin, expressed as a percentage | (Equity / Used Margin) × 100% | Low margin level triggers margin calls or stop-outs |
Margin level tells your broker how “healthy” your account is.
Above 200%: Strong buffer, low risk of margin call.
Around 100%: Margin call zone broker may request more funds.
Below stop-out threshold (often 50% or 20%): Broker automatically closes losing positions.
Scenario:
Equity: $10,000
Used Margin: $2,500
Free Margin = $10,000 – $2,500 = $7,500
Margin Level = ($10,000 / $2,500) × 100% = 400%
Result: Plenty of free margin, safe from margin calls.
If floating losses reduce equity to $3,000:
Free Margin = $3,000 – $2,500 = $500
Margin Level = ($3,000 / $2,500) × 100% = 120%
Now you are close to the margin call threshold one big loss could trigger it.
Many beginners misunderstand what is free margin forex, often confusing it with margin level, which leads to poor risk management. By tracking all three metrics together free margin, used margin, and margin level you can:
Spot margin call risks early
Adjust position sizes before it’s too late
Maintain flexibility to trade during volatility
Knowing what is free margin forex is only useful if you can protect and grow it. The following best practices help keep your account safe and ready for opportunities:
Use conservative leverage – Stick to lower leverage ratios (e.g., 1:10–1:50) to reduce risk and preserve margin.
Control position size – Risk only a small percentage of equity per trade to avoid draining free margin.
Set margin alerts – Receive notifications when free margin drops below your safety threshold.
Close losing trades early – Free up capital before a margin call becomes unavoidable.
Maintain a safety buffer – Keep at least 30–50% of your equity as free margin to handle volatility.
Watch overnight costs – Factor in swaps and fees that can slowly reduce your equity.
Test strategies in demo – Understand how new setups affect free margin before going live.
Protecting free margin is not just about avoiding disaster it’s about keeping enough flexibility to seize the right trades when they appear.
Check out these related forex articles:
Free margin in forex is the amount of money in your account that is not locked in open trades and can be used to open new positions or absorb losses.
Yes. If your losses exceed your equity minus used margin, free margin becomes negative, usually triggering a margin call or stop-out.
You can close losing trades to free up margin, reduce position sizes, or let profitable trades increase equity, which will raise free margin.
Yes. If free margin is low, brokers may restrict withdrawals to prevent your account from falling below required margin levels.
In most cases, yes. Brokers often use these terms interchangeably to describe the funds available for new trades or covering losses.
Ideally before and after every trade, and continuously during volatile market conditions, to avoid margin calls.
Understanding what is free margin forex is essential for protecting your capital and keeping your trading account healthy. It determines how much buying power you have left, how resilient you are to market volatility, and whether you can avoid costly margin calls.
Key takeaways:
Definition: Free margin = Equity – Used Margin.
Purpose: Shows funds available to open new trades or absorb losses.
Importance: Helps prevent margin calls, supports risk management, and maintains trading flexibility.
Best practices: Use conservative leverage, size positions wisely, set margin alerts, and maintain a safety buffer.
Monitoring: Check free margin regularly, especially during volatile sessions.
Mastering free margin is not just about numbers it’s about creating a safety net that allows you to trade confidently and sustainably in any market condition.
Web Tai Chinh is a portal that updates news and information related to finance quickly and accurately, helping users have an overview before investing, clearly understanding concepts and terms related to Finance. Explore more insights in our Forex category, start your FX trading journey today with the right partner for long-term success.
📞 Contact: 055 937 9204
✉️ Email: webtaichinhvnvn@gmail.com
📍 Address: 13 Ho Tung Mau, An Binh, Di An, Binh Duong